BECE 2010 Integrated Science Objective Questions and Answers
Answer all questions in this section.
Each question is followed by four options lettered A to D. Find the correct answer for each question.
1. Water that forms lather readily with soap is said to be
Solution: Soft water lacks minerals like calcium and magnesium, allowing soap to lather easily. Hard water contains these minerals and forms scum.
2. Which of the following life activities are common to both plants and animals?
I. Feeding
II. Locomotion
III. Respiration
Solution: Both plants and animals feed and respire, but locomotion (self-directed movement) is exclusive to animals.
3. A suitable instrument that could be used to measure the internal diameter of a bamboo flute is
Solution: Vernier calipers provide precise measurements of internal diameters, while beam balances measure mass, and metre rules/surveyor’s tapes lack precision.
4. The ability of soils to supply the right amounts of essential nutrients to plants is known as
Solution: Soil fertility specifically refers to the soil’s capacity to provide essential nutrients for plant growth.
5. The simplest way of making well water suitable for laundry purposes is by
Solution: Boiling removes temporary hardness by precipitating calcium carbonate, improving soap lathering. Alum clarifies but doesn’t soften, chlorination disinfects, and filtering removes solids but not dissolved minerals.
6. Washing down of soil nutrients beyond the reach of roots of plants is referred to as
Solution: Leaching involves soluble nutrients being washed downward by water beyond the root zone. Percolation is general water movement, and aeration/infiltration relate to air/water entry into soil.
7. Which of the following statements explain(s) why an object floats in water?
I. is less dense than water
II. is denser than water
III. has the same density as water
Solution: An object floats if its density is less than water (I). If density equals water, it suspends (neutral buoyancy); if denser, it sinks.
8. An example of leafy vegetable crops is
Solution: Lettuce is a leafy vegetable. Cucumber and okro are fruit-vegetables, and onion is a bulb.
9. The structure in the respiratory system of humans where gaseous exchange occurs is
Solution: Alveoli are tiny sacs in the lungs where oxygen and carbon dioxide exchange occurs. Bronchi/trachea/nostrils are airways.
10. The gas produced when glucose is oxidized during internal respiration is
Solution: Glucose oxidation during cellular respiration produces carbon dioxide (carbon (IV) oxide) and water.
11. The farm animal which has crop as part of its digestive system is the
Solution: Birds (e.g., fowl) have a crop for temporary food storage. Goats, pigs, and sheep are ruminants with multi-chambered stomachs.
12. A beneficial effect of wind on the environment is
Solution: Wind aids pollination (anemophily) in plants like grasses. Leaching/erosion are harmful, and wind doesn’t directly promote photosynthesis.
13. The chemical solution that can be used to test for the presence of protein in food substances is
Solution: Millon’s reagent tests for tyrosine in proteins, turning red upon heating. Benedict’s/Fehling’s test for sugars, and iodine for starch.
14. Which of the following statements about bushfires is/are true?
I. They cause air pollution
II. They deplete vegetation cover
III. They contribute to global warming
Solution: Bushfires release pollutants (I), destroy plants (II), and emit CO₂ (a greenhouse gas) contributing to global warming (III).
15. The most effective method of controlling soil erosion on steep slopes is
Solution: Terracing creates level steps on slopes, reducing runoff velocity. Cover cropping/mulching/strip cropping are less effective on steep gradients.
16. Which of the following agencies is responsible for providing information on the weather and climatic conditions of an area?
Solution: Meteorological Services Department specializes in weather/climate data. Other agencies focus on livestock, agriculture outreach, or public information.
17. The farming system which involves the growing of one type of crop on the same piece of land every season is known as
Solution: Monoculture refers to continuous cultivation of a single crop species on the same land. Mono cropping may imply one crop per season but not necessarily recurring.
18. The fifth planet from the sun in the solar system is
Solution: Planetary order: Mercury (1), Venus (2), Earth (3), Mars (4), Jupiter (5), Saturn (6), Uranus (7), Neptune (8).
19. The process that takes place when the sperm and the egg of humans fuse together is referred to as
Solution: Fertilization is the fusion of sperm and egg to form a zygote. Ovulation releases the egg, menstruation sheds the uterine lining, and reproduction is the broader process.
20. The process by which water vapour moves through the stomata of leaves into the atmosphere is known as
Solution: Transpiration is water loss via leaf stomata. Absorption is water uptake by roots, diffusion is passive molecular movement, and osmosis is water diffusion across membranes.
21. An example of intensive system of poultry keeping is the
Solution: The deep litter system confines birds indoors with litter bedding (intensive). Fold unit/free range/free-running are extensive systems with outdoor access.
22. The symbol represents
Solution: The symbol is identified as an \( n-p-n \) transistor.
23. The part of the diagram labelled I has
Solution: For an \( n-p-n \) transistor (Q22), the base (labeled I) is \( p \)-type, with holes as majority carriers.
24. A spot made on a white paper with a given food substance turned the spot on the paper translucent. The food substance is likely to contain
Solution: Oils/lipids create translucent spots on paper (grease-spot test). Glucose/protein/starch do not.
25. Which of the following sources of energy is non-renewable?
Solution: Per the available options, wood is the answer
26. Which of the following farm animals is / are housed in a hutch?
I. Goats
II. Pigs
III. Rabbits
Solution: A hutch is a cage for rabbits. Goats/pigs are housed in pens/stalls.
27. Which of the following blood vessels carries deoxygenated blood?
Solution: Pulmonary artery carries deoxygenated blood from the heart to the lungs. Aorta/renal artery carry oxygenated blood; pulmonary vein carries oxygenated blood to the heart.
28. The energy transformation that takes place in a car battery is
Solution: When powering lights, the battery converts chemical energy to electrical energy, which is then transformed to light energy.
29. The type of liquid suitable to construct a thermometer to read temperatures of about 150°C is
Solution: Mercury has a high boiling point (357°C) and remains liquid at 150°C. Alcohol (78°C) and water (100°C) boil below 150°C; turpentine (~160°C) is less stable.
30. Amino acids are the end-products of the digestion of
Solution: Proteins are broken down into amino acids by proteases. Carbohydrates yield sugars; fats/oils yield fatty acids/glycerol.
31. The type of teeth used by mammals to cut food materials is
Solution: Incisors cut food (e.g., biting). Canines tear, molars/premolars grind.
32. Fishponds are often stocked using
Solution: Fingerlings (juvenile fish) are hardy and ideal for stocking. Fry/eggs are less resilient; anchovies are a species, not a life stage.
33. Which of the following processes result(s) in the formation of a new substance?
I. Burning of wood
II. Rusting of iron nail
III. Heating water into vapour
Solution: Burning (combustion) and rusting (oxidation) form new substances. Heating water to steam is a physical change (state change only).
34. The use of resistant breeds of farm animals in controlling diseases is a
Solution: Resistant breeds leverage biological mechanisms (e.g., genetics) to combat diseases. Chemical/cultural/physical methods involve external interventions.
35. A load of 10 N is moved through a distance of 2 m. Calculate the work done.
Solution: Work = Force × Distance = 10 N × 2 m = 20 J.
36. Which of the following components of human blood is dissolved in the plasma?
Solution: Mineral salts (electrolytes) are dissolved in plasma. Phagocytes, platelets, and RBCs are cellular components.
37. An atom of carbon is represented as \( ^{12}_{6}C \). How many neutrons are in the nucleus of the carbon atom?
Solution: Neutrons = Mass number (12) – Atomic number (6) = 6.
38. In agribusiness, middlemen operate within the
Solution: Middlemen (e.g., wholesalers, retailers) distribute goods through the supply chain, linking producers to consumers.
39. Which of the following illustrations shows the correct direction of the lines of force around a bar magnet?
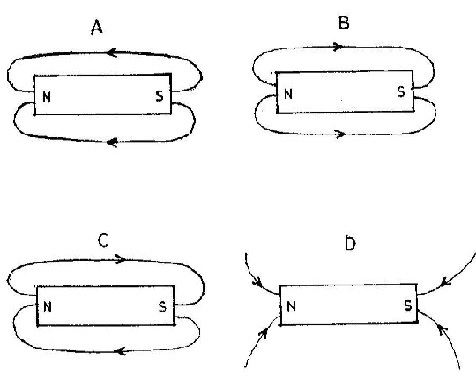
Solution:Option B shows field lines emerging from the North pole and entering the South pole externally.
40. The human sex cells are produced in the
Solution: Sperm are produced in testes; eggs in ovaries. Scrotum holds testes, uterus hosts fetal development, and penis/vagina are copulatory organs.
1. Question 1
1. (a) The diagram below is used to demonstrate an activity in the laboratory.
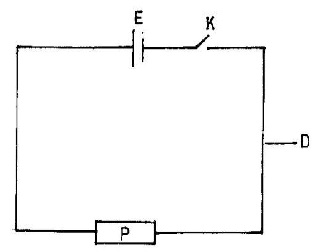
Study it carefully and use it to answer the questions that follow:
(i) What does the diagram represent?
(ii) Identify the components labelled D, E, K and P in the diagram.
(iii) State one function each of the parts labelled D, E, K and P.
(iv) Mention the energy transformation that occurs in E in the diagram when K is closed.
(b) In an experiment, red and blue litmus papers were dipped separately into three test tubes each containing one of the test substances listed in the table below.
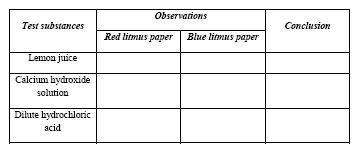
(i) Copy and complete the table by making the necessary observation and conclusion for each substance.
(ii) Name two of the test substances that would react with each other to produce salt and water.
(iii) Write down a balanced chemical equation for the reaction in (ii) above.
(c) The diagram below is an illustration of the human digestive system. Study it carefully and use it to answer the questions that follow:
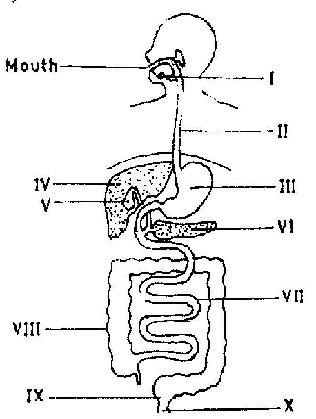
(i) Name the parts labelled I, II, III and IV.
(ii) State one function of each of the parts labelled V and VI.
(iii) Name the part where the digestion of protein starts.
(iv) Identify the part where:
(a) absorption of end-products of digestion takes place
(b) re-absorption of water takes place
(c) egestion takes place
(d) The diagram below is an illustration of a simple farm tool.
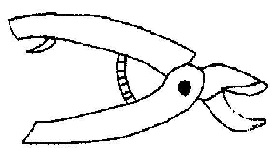
Study it carefully and use it to answer the questions that follow:
(i) Identify the tool.
(ii) State three uses of the tool.
(iii) Mention three ways of maintaining the tool.
Solutions for Question 1
(a) (i) An electrical circuit
(ii)
- D: Conductor wire
- E: Cell or emf source
- K: Switch or key
- P: Resistor
(iii)
- D: Conducts electricity (electric current flows through it)
- E: Provides electromotive force (emf) / Converts chemical energy to electrical energy
- K: Opens or closes the circuit / Controls current flow
- P: Opposes current flow / Converts electrical energy to other forms
(iv) Chemical energy → Electrical energy
(b) (i)
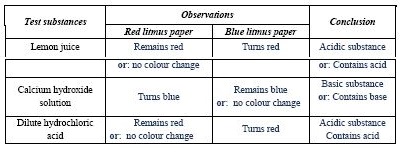
(ii) Calcium hydroxide solution and dilute hydrochloric acid
(iii) \(\text{Ca(OH)}_2 + 2\text{HCl} \rightarrow \text{CaCl}_2 + 2\text{H}_2\text{O}\)
(c) (i)
- I: Salivary gland
- II: Oesophagus (gullet)
- III: Stomach
- IV: Liver
(ii)
- V: Stores bile / Concentrates bile
- VI: Secretes digestive enzymes into small intestine / Secretes insulin into bloodstream
(iii) Stomach (Part III)
(iv)
(a) Small intestine (Part VII)
(b) Large intestine (Part VIII)
(c) Anus (Part X)
(d) (i) Secateurs (pair of secateurs)
(ii)
- Trimming plants
- Cutting branches
- Pruning crops
(iii)
- Oil/grease metal parts
- Wash and dry after use
- Tighten loose bolts/nuts
- Sharpen cutting edges
2. Question 2
2. (a) (i) What is neutralization reaction?
(ii) Write a balanced chemical equation for the reaction between each of the following pairs of substances:
(a) Sodium metal and dilute hydrochloric acid.
(b) Sodium hydroxide and dilute hydrochloric acid.
(b) Explain weaning as used in animal production.
(c) (i) What is Milky Way?
(ii) State one use of artificial satellites.
(d) (i) What is a habitat?
(ii) Give two examples of a habitat.
SOLUTIONS FOR QUESTION 2
(a) (i) Reaction between acid and base to produce salt and water
(ii) (a) \(2\text{Na} + 2\text{HCl} \rightarrow 2\text{NaCl} + \text{H}_2\)
(b) \(\text{NaOH} + \text{HCl} \rightarrow \text{NaCl} + \text{H}_2\text{O}\)
(b) Transitioning young animals from mother's milk to solid food
(c) (i) The spiral galaxy containing Earth's solar system
(ii) Weather forecasting / Telecommunications / GPS navigation / Earth observation
(d) (i) Natural home/environment of an organism
(ii) Forest / River / Desert / Ocean / Grassland
3. Question 3
3. (a) (i) Define pressure.
(ii) Explain why it is important to sharpen a knife before use.
(b) (i) State two differences between metals and non-metals.
(ii) What is an alloy?
(iii) Mention the components of each of the following alloys:
(a) steel
(b) brass
(c) Mention three conditions suitable for rearing tilapia in a fishpond.
(d) Explain how the streamlined body of a bony fish enables it to live successfully in water.
SOLUTIONS FOR QUESTION 3
(a) (i) Force per unit area (\( \text{Pressure} = \frac{\text{Force}}{\text{Area}} \))
(ii) Sharpening reduces surface area → increases pressure → cuts efficiently with less force
(b) (i)
Metals: High melting point, Shiny (lustrous), Malleable, Good conductors
Non-metals: Low melting point, Dull, Brittle, Poor conductors
(ii) Homogeneous mixture of metals (e.g., metal + metal/non-metal)
(iii) (a) Steel: Iron + Carbon
(b) Brass: Zinc + Copper
(c)
- Clean, non-polluted water
- Optimal temperature (20–30°C)
- Adequate dissolved oxygen
- Suitable pH (6.5–9.0)
- Proper salinity
(d) Reduces water resistance → efficient swimming / energy conservation
4. Question 4
4. (a) (i) What is a disease vector?
(ii) Mention two methods of controlling each of the following types of pests of farm animals:
(a) ectoparasites
(b) endoparasites
(b) (i) State two symptoms of nitrogen deficiency in a tomato plant.
(ii) Describe side dressing as a method of fertilizer application.
(c) (i) Define power.
(ii) State the S.I. unit of power.
(d) Draw the electronic structure of sulphur (Atomic number = 16).
SOLUTIONS FOR QUESTION 4
(a) (i) Organism transmitting pathogens or An organism that transmits disease-causing microorganisms from an infected person oranimal to another (e.g., mosquito, tick)
(ii) (a) Ectoparasites: Pesticides / Dipping / Dusting / Handpicking
(b) Endoparasites: Deworming / Vaccination / Feed rotation / Sanitation
(b)
(i) Yellowing leaves / Stunted growth / Weak stems / Small fruits
(ii) Applying fertilizer beside crops (along plant rows) during growth phase
(c) (i) Work done per unit time (\( \text{Power} = \frac{\text{Work}}{\text{Time}} \))
(ii) Watt (W)
(d) Electronic configuration:
- Shell 1: 2 electrons
- Shell 2: 8 electrons
- Shell 3: 6 electrons
(2.8.6 configuration)
5. Question 5
5. (a) (i) What is respiration?
(ii) Name the types of respiration that occur in humans.
(b) List three ways of maintaining soil fertility.
(c) (i) Write the systematic name of each of the following chemical compounds:
(a) FeS
(b) SO₂
(c) CO₂
(ii) Give one reason why copper, silver, and gold are mostly used in making ornaments and jewellery.
(d) (i) What is a fuse?
(ii) Explain why a fuse is used in an electrical circuit.
Solutions for Question 5
(a)
(i) Breakdown of food to release energy, CO₂, and water
(ii) External respiration / Internal respiration / Aerobic respiration / Anaerobic respiration
(b)
- Crop rotation
- Composting
- Mulching
- Fertilizer application
- Bush fallowing
- Green manuring
(c) (i)
(a) Iron(II) sulphide
(b) Sulphur(IV) oxide
(c) Carbon(IV) oxide
(ii) High lustre / Malleability / Ductility / Corrosion resistance
(d) (i) Safety device with metal wire that melts during overcurrent
(ii) Breaks circuit during power surges → prevents fire/damage to appliances
6. Question 6
6. (a) (i) What is the difference between unicellular organism and multicellular organism?
(ii) State two reasons why vegetable crops are important to humans.
(b) (i) State two elements of climate.
(ii) What is the difference between climate and weather?
(c) Mention three advantages of staking in crop production.
(d) Explain each of the following processes:
(i) corrosion;
(ii) sublimation.
Solutions for Question 6
(a) (i)
Unicellular: Single-celled organism, Simple body organization
Multicellular: Many-celled organism, Complex body organization
(ii) Source of vitamins / Dietary fiber / Minerals / Adds flavor to food
(b) (i) Rainfall / Temperature / Humidity / Wind / Sunshine
(ii)
Climate: Long-term atmospheric patterns (years), Average of weather conditions
Weather: Short-term atmospheric conditions (days), Current state of atmosphere
(c)
- Prevents fruit/vegetable contact with soil
- Facilitates weeding/harvesting
- Improves air circulation around plants
- Reduces disease incidence
- Supports plant growth during fruiting
(d) (i) Gradual destruction of materials (especially metals) by chemical reactions with environment (e.g., rusting of iron)
(ii) Direct phase change from solid to gas without liquid state (e.g., dry ice → CO₂ gas, mothballs → vapor)